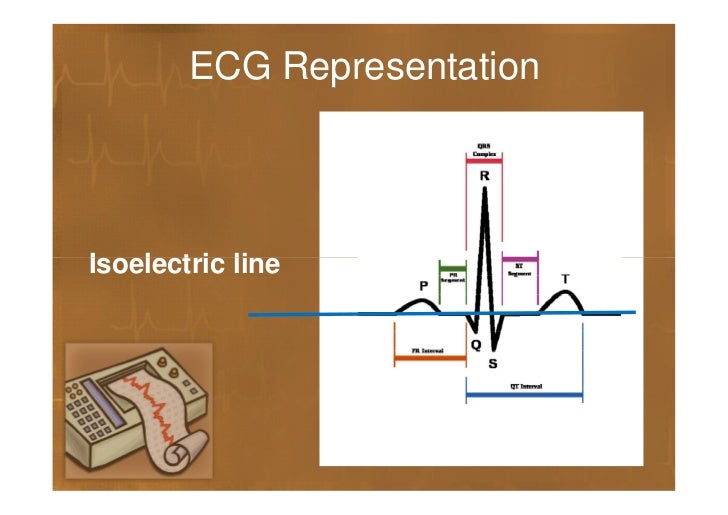
The isoelectric line on an electrocardiogram (ECG) is a horizontal line that represents the electrical neutrality of the heart. It is located at the midpoint between the positive and negative deflections of the ECG waveform. The isoelectric line is used as a reference point for measuring the amplitude of the ECG waves and for determining the heart rate.
The isoelectric line is not always perfectly flat. It may be slightly elevated or depressed, depending on the electrical activity of the heart. For example, the isoelectric line may be elevated in patients with atrial fibrillation, which is a condition in which the atria of the heart beat irregularly. The isoelectric line may also be depressed in patients with ventricular tachycardia, which is a condition in which the ventricles of the heart beat too fast.
What is the Isoelectric Line on an ECG?
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphical representation of the electrical activity of the heart. It is used to diagnose a number of heart conditions, including arrhythmias, heart attacks, and heart failure.
The ECG is made up of a series of waves that correspond to the different electrical events that occur during the heart's cycle. The isoelectric line is the horizontal line that runs through the middle of the ECG. It represents the point at which there is no electrical activity in the heart.
The isoelectric line is important because it provides a reference point for measuring the other waves on the ECG. The height of the waves is measured from the isoelectric line, and the width of the waves is measured from the beginning of one wave to the beginning of the next wave.
The isoelectric line can also be used to identify arrhythmias. An arrhythmia is a heart rhythm that is abnormal. Arrhythmias can be caused by a number of factors, including heart disease, electrolyte imbalances, and medications.
If you are having any symptoms of heart disease, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or palpitations, it is important to see your doctor for an ECG. An ECG can help your doctor diagnose any heart problems that you may have and recommend the appropriate treatment.
Sub-section 1: What does the isoelectric line represent?
The isoelectric line represents the point at which there is no electrical activity in the heart.
It is important because it provides a reference point for measuring the other waves on the ECG. The height of the waves is measured from the isoelectric line, and the width of the waves is measured from the beginning of one wave to the beginning of the next wave.
Sub-section 2: How can the isoelectric line be used to identify arrhythmias?
Arrhythmias are heart rhythms that are abnormal. Arrhythmias can be caused by a number of factors, including heart disease, electrolyte imbalances, and medications.
The isoelectric line can be used to identify arrhythmias by looking for changes in the shape or timing of the waves on the ECG.
What Is The Isoelectric Line On An ECG
The isoelectric line on an electrocardiogram (ECG) is the baseline that represents the electrical neutrality of the heart. It is typically a flat line that runs through the middle of the ECG waveform.
Significance of the Isoelectric Line
The isoelectric line is essential for measuring the electrical activity of the heart because it provides a reference point from which all other electrical activity is measured. The electrical impulses that cause the heart to contract are represented as deflections from the isoelectric line. These deflections are known as waves and are labeled P, Q, R, S, and T. Each wave corresponds to a specific electrical event in the heart.
Variations in the Isoelectric Line
The isoelectric line can vary slightly from person to person. This is due to differences in the size, shape, and position of the heart. It can also be affected by factors such as temperature, blood pressure, and medications.
Abnormal Isoelectric Line
An abnormal isoelectric line can indicate a number of underlying conditions. These include:
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Hormonal disorders
- Heart disease
- Lung disease
- Neuromuscular disorders
If you have an abnormal isoelectric line on your ECG, it is important to see a doctor to determine the underlying cause.
What is the Significance of the Isoelectric Line on an ECG?
The isoelectric line on an ECG is the baseline from which the waves of the ECG are measured. It represents the electrical balance of the heart, where the positive and negative charges are equal. The isoelectric line is typically drawn as a horizontal line on the ECG tracing.
The isoelectric line is important for interpreting the ECG because it helps to identify the different waves of the ECG and to determine the electrical activity of the heart. The waves of the ECG are labeled as P, Q, R, S, and T. The P wave represents the electrical activity of the atria, the Q wave represents the electrical activity of the ventricles, the R wave represents the electrical activity of the ventricles, the S wave represents the electrical activity of the ventricles, and the T wave represents the electrical activity of the ventricles.
The isoelectric line helps to identify the different waves of the ECG because the waves are measured from the isoelectric line. The P wave is measured from the isoelectric line to the top of the P wave, the Q wave is measured from the isoelectric line to the bottom of the Q wave, the R wave is measured from the isoelectric line to the top of the R wave, the S wave is measured from the isoelectric line to the bottom of the S wave, and the T wave is measured from the isoelectric line to the top of the T wave.
The isoelectric line is significant for interpreting the ECG because it helps to determine the electrical activity of the heart. The isoelectric line represents the electrical balance of the heart, where the positive and negative charges are equal. If the isoelectric line is shifted above or below the baseline, it can indicate an abnormality in the electrical activity of the heart.
For example, if the isoelectric line is shifted above the baseline, it can indicate an increased number of positive charges in the heart. This can be caused by a number of factors, such as an increased number of sodium ions in the heart or an increased number of calcium ions in the heart.
If the isoelectric line is shifted below the baseline, it can indicate an increased number of negative charges in the heart. This can be caused by a number of factors, such as an increased number of potassium ions in the heart or an increased number of magnesium ions in the heart.
How is the Isoelectric Line Measured on an ECG?
The isoelectric line on an ECG is the baseline from which all other electrical activity is measured. It represents the electrical neutrality of the heart, when there is no electrical activity occurring. The isoelectric line is typically measured at the midpoint between the P and T waves.
To measure the isoelectric line, first identify the P wave and T wave. The P wave is the first positive deflection on the ECG, and the T wave is the last positive deflection. Once you have identified the P and T waves, find the midpoint between them. This is the isoelectric line.
The isoelectric line is important for interpreting an ECG because it provides a reference point for all other electrical activity. By measuring the distance between the isoelectric line and other electrical events, such as the QRS complex, doctors can determine the timing and duration of these events. This information can be used to diagnose heart conditions, such as arrhythmias and heart blocks.
In addition to measuring the isoelectric line, doctors may also measure the amplitude of the ECG waves. The amplitude is the height of the waves, and it can be used to determine the strength of the electrical activity. The amplitude of the ECG waves can be affected by a number of factors, including the thickness of the heart wall, the size of the heart, and the presence of any heart disease.
What Can the Isoelectric Line Tell Us?
The isoelectric line on an ECG is the baseline that represents the electrical neutrality of the heart. It is the point at which the positive and negative charges in the heart cancel each other out. The isoelectric line is used as a reference point for measuring the electrical activity of the heart.
The isoelectric line can tell us a lot about the heart's electrical activity. For example, it can tell us:
- The heart rate
- The rhythm of the heart
- The presence of any abnormalities in the heart's electrical activity
The heart rate can be determined by measuring the time between two consecutive QRS complexes. The QRS complex is the deflection on the ECG that represents the depolarization of the ventricles. The normal heart rate is 60-100 beats per minute.
The rhythm of the heart can be determined by looking at the pattern of the QRS complexes. A regular rhythm means that the QRS complexes are evenly spaced. An irregular rhythm means that the QRS complexes are not evenly spaced.
The presence of any abnormalities in the heart's electrical activity can be determined by looking for any deviations from the normal pattern of the ECG. For example, a prolonged PR interval may indicate a conduction delay in the heart. A widened QRS complex may indicate a ventricular hypertrophy.
The isoelectric line is a valuable tool for assessing the heart's electrical activity. It can help us to diagnose a variety of heart conditions, including arrhythmias, conduction disturbances, and myocardial ischemia.
What Happens When the Isoelectric Line is Abnormal?
When the Isoelectric line is abnormal, it can indicate a number of different conditions. These include:
An Electrical Abnormality in the Heart
This could be caused by a number of things, such as a heart attack, heart failure, or an arrhythmia.
Electrolyte Imbalances
This can be caused by dehydration, excessive sweating, or certain medications.
Metabolic Disorders
These can include diabetes or thyroid problems.
If you have an abnormal isoelectric line on your ECG, it is important to see a doctor to determine the cause. Treatment will depend on the underlying condition.
Conclusion
The isoelectric line on an ECG is a baseline that represents the electrical neutrality of the heart. It is used as a reference point for measuring the amplitude of the ECG waves. The isoelectric line is typically located at the center of the ECG tracing, between the P wave and the QRS complex.
The isoelectric line can be affected by a number of factors, including the position of the electrodes, the patient's heart rate, and the presence of any electrical interference. It is important to note that the isoelectric line is not always perfectly flat, and it may vary slightly from one ECG tracing to another.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the isoelectric line on an ECG?
The isoelectric line is a horizontal line on an electrocardiogram (ECG) that represents the point at which the electrical activity of the heart is equal in both directions. It is typically located at the middle of the ECG tracing and serves as a reference point for measuring the amplitudes of the ECG waves.
2. What does the isoelectric line indicate?
The isoelectric line indicates the electrical neutrality of the heart. When the heart is at rest, there is no net electrical charge flowing across the heart, and the isoelectric line represents this electrical equilibrium.
3. How is the isoelectric line used in ECG interpretation?
The isoelectric line helps to identify the different waves of the ECG. The P wave, QRS complex, and T wave are measured relative to the isoelectric line. Deviations from the isoelectric line can indicate electrical abnormalities in the heart.
4. What can cause deviations from the isoelectric line?
Deviations from the isoelectric line can be caused by various electrical disturbances in the heart. These disturbances can include arrhythmias, electrolyte imbalances, and certain medications.
5. Why is the isoelectric line important in ECG interpretation?
The isoelectric line is an important reference point for interpreting ECGs. It helps to identify the different waves of the ECG and assess their amplitudes. Deviations from the isoelectric line can provide valuable information about the electrical activity of the heart and help diagnose various cardiac conditions.